 |
HOME CONSERVATION C-TERMINAL ANALYSES DNA AND RNA SEQUENCES RESEARCH QUESTIONS RESULTS RESOURCES REFERENCES |
|
Protein truncating variants in the gene ZNF292 have been implicated in several neurodevelopmental disorders. Although the phenotype is quite broad ASD, ADHD and ID/DD are common features (Mirzaa, 2019). The only work done on the function of ZNF292 in the nervous system to-date shows it acts an enhancer for the growth hormone gene GH1 in somatotrophs ( Lipkin 1993). It is also expressed in other areas of the brain including the hippocampus and cerebellar cortex. ZNF292 has also been found to be mutated in several cancers suggesting a role as a repressor. Other reports point to its involvement in cell type maintenance and a circular RNA (circRNA) derived from the ZNF292 gene has been implicated in endothelial cell response to hypoxia (Boeckel 2015). ZNF292 has also been shown to co-precipitate with the heterochromatin protein CBX3 (HP1γ, Ostapcuk 2018). Structure ZNF292 is a highly conserved C2H2 zinc finger protein containing sixteen fingers. Most proteins in this class have one or more tandem arrays of zinc fingers placed within 5-7 aa apart that cooperate in binding to specific DNA sequences. ZNF292 has two such modules (finger 1-2 and fingers 5-7) but no DNA binding activity has been demonstrated for them. The remaining fingers are farther apart putting it into the class of widely-spaced zinc finger proteins as typified by proteins like WIZ. Only three of its zinc fingers (10-12) have been implicated in DNA binding. It does so cooperatively with POU1F1 (Pit-1) at the GH1 promoter. The others may instead be involved in RNA or protein interactions. 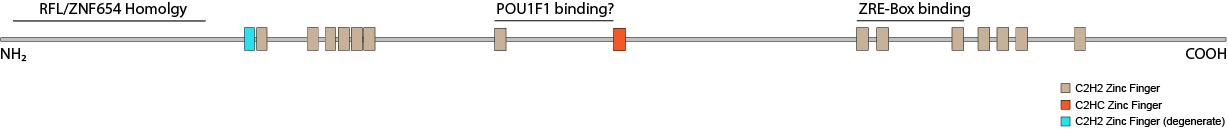
ZNF292’s closest paralogs are RLF and ZNF654. Though both vary considerably in their larger C-terminal, zinc finger-containing domains, they have highly similar N-terminal domains. RLF has been implicated in maintaining hypomethylatation at CpG shores at a number of promoters. The homology between the N-terminal regions of all three proteins suggest a similar function but for a different subsets of gene promoters. RLF also co-precipitates with heterochromatin proteins CBX1 (HP1β), CBX5 (HP1α) and CBX3 (HP1γ). All three proteins share a gene structure wherein a single large exon encodes all of the C-terminal zinc fingers and a number of small exons encode the N-terminal domain. This structure may make them particularly susceptible to pathogenic protein truncating variants because terminal exons generally escape nonsense-mediated decay. 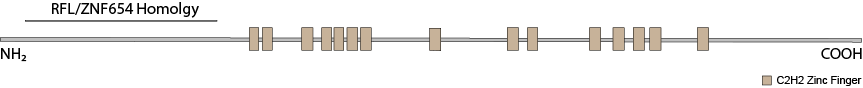
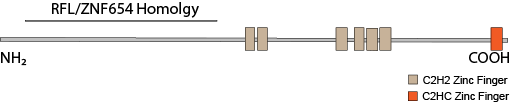
Impact of Protein Truncating Variants Both ZNF292 and RLF have a probability of loss intolerance (pLI) of 1.0 in the ExAC database browser. ZNF654 has a pLI of 0.95. Cassa (2017) Studied the effects of heterozygous protein-truncating variants from human exome data and ranked genes according to a genome-wide distribution of selective effects for heterozygous PTVs (shet). All three genes ranked in the top quintile with very high probabilities of autosomal dominance (pAD).
|